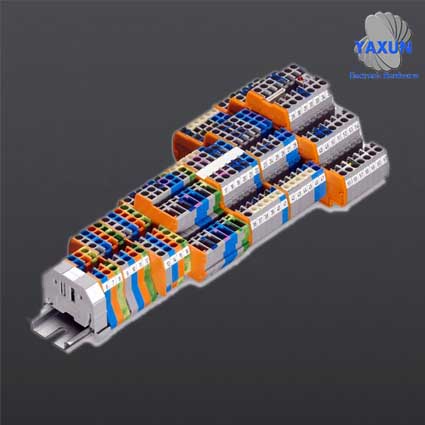
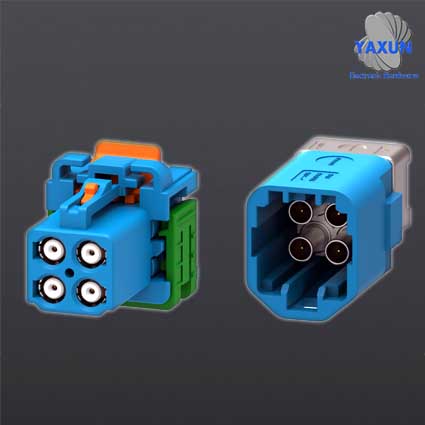
Standard Specification for Sharing and Exchange of Data Bus Connectors
- PRODUCT DETAIL
Bus refers to a standardized way of exchanging data between computer components, that is, providing data transmission and control logic for each component in a universal way. From another point of view, if the Mother Board is a city, then the bus is like a bus in the city, which can transmit bits that go back and forth continuously according to a fixed driving route. These lines can only transmit one bit at the same time. Therefore, multiple lines must be used at the same time to send more data, and the number of data that the bus can transmit at the same time is called width. In terms of bits, the larger the bus width, the better the transmission performance. The bus bandwidth (that is, the total number of data that can be transmitted per unit time) is: bus bandwidth = frequency × width (Bytes/sec).
1. Data exchange of system entities:
Each subsystem has a business entity layer on the architectural layering, and the data exchange mechanism establishes a layer that is transparent to all application systems at the business entity layer. Between subsystems, no matter what the specific technical solution they implement, they can share and interact through the business entity layer. This also establishes a structure that can carry out continuous integration and business expansion among subsystems, thereby realizing a scalable and complete integrated information system.
2. WebService data exchange, in the case of heterogeneous sub-systems, where data is not centralized, effective technical means must be used to ensure heterogeneous data sharing and exchange. WebService is a standard Web-based service, which is not limited by the transmission protocol or hardware, nor by the specific implementation technology of the subsystem. And more advanced and complete application systems or products provide integrated interfaces based on WebService. This solves the data sharing and exchange between heterogeneous subsystems. WebService can also solve the data exchange across networks and industry systems, which requires the counterparty interface unit to also have WebService services.
3. Formatted file data exchange, which is to transfer files with external systems, business internal systems and external information exchange requirements, require the provision of corresponding data sharing and exchange technical mechanisms. Such problems are usually solved using technical solutions based on file systems, such as file submission and file exchange. An example can be used to illustrate: real-time and non-real-time data exchange exists among taxation, treasury, and silver. This exchange optimization scheme is to use files to exchange through Socket. The realization of this type of technology generally uses the underlying technology.
The bandwidth of the bus refers to the amount of data transmitted on the bus per unit time, that is, the maximum steady-state data transmission rate of MB transmitted per second. Two factors closely related to the bus are the bit width of the bus and the operating frequency of the bus. The relationship between them:
Bus bandwidth = bus operating frequency * bus bit width/8
2. The bit width of the bus
The bit width of the bus refers to the number of bits of binary data that the bus can transmit at the same time, or the number of bits of the data bus, that is, the concept of bus widths such as 32 bits and 64 bits. The wider the bit width of the bus, the greater the data transfer rate per second, and the wider the bandwidth of the bus.
3. Operating frequency of the bus
The working clock frequency of the bus is in MHZ. The higher the working frequency, the faster the bus working speed and the wider the bus bandwidth.

Share and exchange
The data bus standardizes the implementation methods of data sharing and exchange in homogeneous systems and heterogeneous systems in a large integrated application system, as well as data exchange standards between systems. It can be used to transfer information between microprocessor and memory, microprocessor and input and output interfaces. The width of the data bus is an important indicator that determines computer performance. The data bus of the microcomputer is mostly 32-bit or 64-bit.1. Data exchange of system entities:
Each subsystem has a business entity layer on the architectural layering, and the data exchange mechanism establishes a layer that is transparent to all application systems at the business entity layer. Between subsystems, no matter what the specific technical solution they implement, they can share and interact through the business entity layer. This also establishes a structure that can carry out continuous integration and business expansion among subsystems, thereby realizing a scalable and complete integrated information system.
2. WebService data exchange:
It is a Web service standard, which provides a solution for sharing and exchanging data between heterogeneous systems. It can also be used to use a unified interface standard for data sharing and exchange in product integration.
It is a Web service standard, which provides a solution for sharing and exchanging data between heterogeneous systems. It can also be used to use a unified interface standard for data sharing and exchange in product integration.

Exchange method
1. Data exchange at the business entity layer, which is the most direct and efficient exchange scheme between homogeneous subsystem systems. By defining the data object interface layer between the similar subsystems, transmitting through DTO, or directly connecting or accessing data tables in the database, the data sharing and exchange between similar subsystems can be achieved. For example, data sharing and exchange between various subsystems in the collection management system, data sharing between business systems and data mining.2. WebService data exchange, in the case of heterogeneous sub-systems, where data is not centralized, effective technical means must be used to ensure heterogeneous data sharing and exchange. WebService is a standard Web-based service, which is not limited by the transmission protocol or hardware, nor by the specific implementation technology of the subsystem. And more advanced and complete application systems or products provide integrated interfaces based on WebService. This solves the data sharing and exchange between heterogeneous subsystems. WebService can also solve the data exchange across networks and industry systems, which requires the counterparty interface unit to also have WebService services.
3. Formatted file data exchange, which is to transfer files with external systems, business internal systems and external information exchange requirements, require the provision of corresponding data sharing and exchange technical mechanisms. Such problems are usually solved using technical solutions based on file systems, such as file submission and file exchange. An example can be used to illustrate: real-time and non-real-time data exchange exists among taxation, treasury, and silver. This exchange optimization scheme is to use files to exchange through Socket. The realization of this type of technology generally uses the underlying technology.
Technical index
1. The bandwidth of the bus (bus data transfer rate)The bandwidth of the bus refers to the amount of data transmitted on the bus per unit time, that is, the maximum steady-state data transmission rate of MB transmitted per second. Two factors closely related to the bus are the bit width of the bus and the operating frequency of the bus. The relationship between them:
Bus bandwidth = bus operating frequency * bus bit width/8
2. The bit width of the bus
The bit width of the bus refers to the number of bits of binary data that the bus can transmit at the same time, or the number of bits of the data bus, that is, the concept of bus widths such as 32 bits and 64 bits. The wider the bit width of the bus, the greater the data transfer rate per second, and the wider the bandwidth of the bus.
3. Operating frequency of the bus
The working clock frequency of the bus is in MHZ. The higher the working frequency, the faster the bus working speed and the wider the bus bandwidth.











