Causes of failure of high-voltage cables

The high-voltage cable is a bridge between the power supply equipment and the electrical equipment, and plays the role of transmitting electric energy. It is widely used, so faults often occur. The following is a brief analysis of the causes of common problems with high-voltage cables. According to the cause of the fault, it can be classified into the following categories: Manufacturer manufacturing reasons, laying process quality reasons, design unit design reasons, external force damage, etc.
Manufacturer manufacturing reason
Manufacturers' manufacturing reasons are divided into cable body reasons, cable joint reasons, and cable grounding system according to different locations.
Reasons for cable body manufacturing
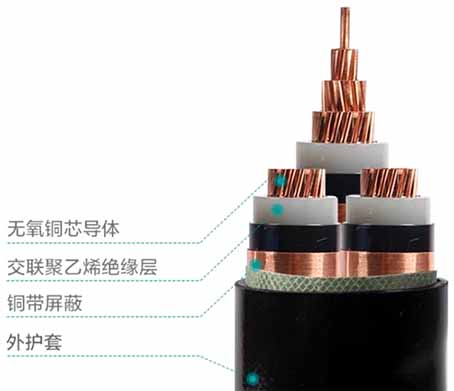
Generally, the problems that are likely to occur in the cable production process are: Insulation eccentricity, uneven insulation shield thickness, impurities in the insulation, protrusions on the inner and outer shields, uneven cross-linking, dampness of the cable, poor sealing of the cable metal sheath, etc. Some cases are more serious and may fail during the completion test or soon after being put into operation. Most of them exist in the form of defects in the cable system, causing serious hidden dangers to the long-term safe operation of the cable.
Reasons for manufacturing cable joints
In the past, high-voltage cable joints used wrap-around, die-cast, and molded-in types, which required a lot of work on site. And because of the limitation of the site conditions and the manufacturing process, there will inevitably be air gaps and impurities between the insulating tape layers, so problems are prone to occur. The commonly used types in China are assembled and prefabricated types.
Cable joints are divided into cable terminal joints and cable intermediate joints. Regardless of the joint form, cable joint failures generally appear at the cable insulation shielding fracture, because this is where the electrical stress is concentrated. The reasons for the failure of the cable joint due to manufacturing reasons include the manufacturing defect of the stress cone body, the problem of the insulating filler, and the oil leakage of the sealing ring.
Cable grounding system
The cable grounding system includes cable grounding box, cable grounding protection box (with protective layer protector), cable cross interconnection box, protective layer protector and other parts. Generally, the problem that is prone to occur is mainly because the box body is not well sealed and the water enters the ground, which causes the metal sheath to induce excessive current. In addition, the parameter selection of the protective layer protector is not reasonable or the quality is not good. The instability of zinc oxide crystals can easily cause damage to the protective layer.
Reasons for the quality of cable laying facilities
There are many examples of high-voltage cable system failures due to the quality of the installation process. The main reasons are as follows:
First, the site conditions are relatively poor: the environment and process requirements for cables and connectors are very high when they are manufactured in the factory, and the temperature, humidity, and dust on the construction site are difficult to control.
The second is that small slip marks will inevitably be left on the insulating surface during cable construction. Semi-conductive particles and sand on the emery cloth may also be embedded in the insulation. In addition, since the insulation is exposed to the air during the construction of the joint, moisture will be absorbed in the insulation, which will leave hidden dangers for long-term safe operation.
The third is that the cable installation did not strictly follow the process construction or process regulations, and did not consider the possible problems.
Fourth, the DC withstand voltage test is used for the completion acceptance test, which causes the formation of a back electric field in the joint and leads to insulation damage.
Fifth, it is caused by improper sealing treatment. The intermediate joint must adopt a sealed structure with a metal copper shell and a PE or PVC insulating anti-corrosion layer. Ensure the tightness of the lead seal during on-site construction, which effectively guarantees the sealing and waterproof performance of the joint.
Design reasons for high-voltage cables
Breakdown caused by cable squeezing caused by thermal expansion of the cable. When the load of the cross-linked cable is high, the temperature of the core rises and the cable expands due to heat. At the turning point in the tunnel, the cable is topped on the vertical surface of the support, and the creep force of the long-term large-load operation of the cable is large. As a result, the vertical surface of the bracket crushes the outer sheath of the cable, and the metal sheath squeezes into the cable insulation layer to cause cable breakdown.





